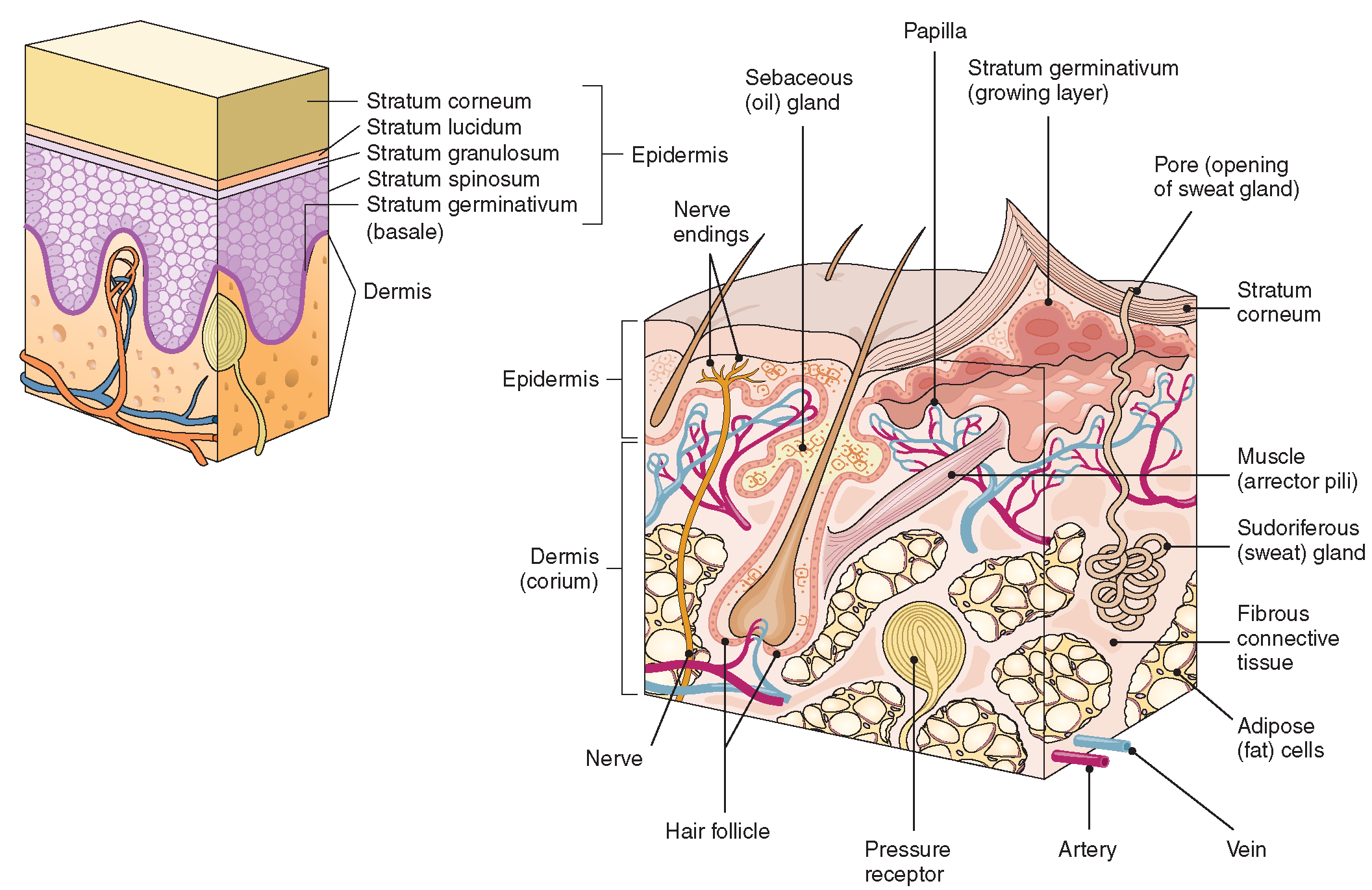
The Integumentary System (Structure and Function) (Nursing) Part 1
Stratum basale, also known as stratum germinativum, is the deepest layer, separated from the dermis by the basement membrane (basal lamina) and attached to the basement membrane by hemidesmosomes. The cells found in this layer are cuboidal to columnar mitotically active stem cells that are constantly producing keratinocytes.
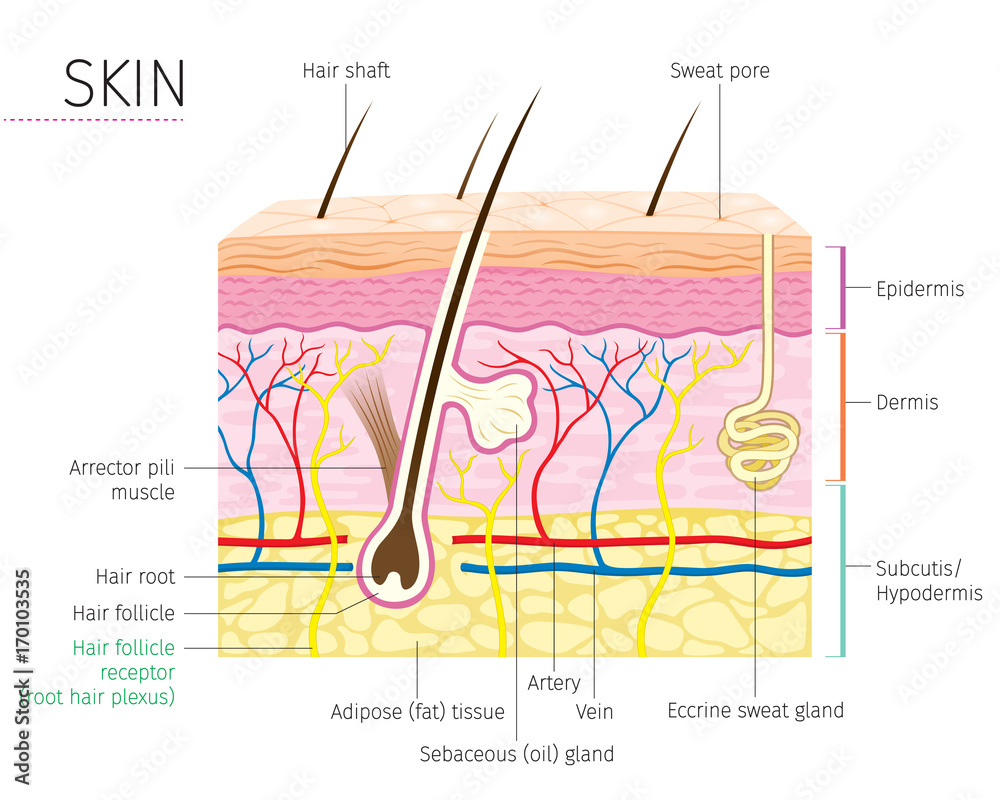
Skin Diagram Labeled
The skin is composed of two main layers: the epidermis, made of closely packed epithelial cells, and the dermis, made of dense, irregular connective tissue that houses blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures. Beneath the dermis lies the hypodermis, which is composed mainly of loose connective and fatty tissues.

Diagram of human skin layers Charlotte Desire
Layers of Skin: How Many, Diagram, Model, Anatomy, In Order The Layers of Your Skin Your skin includes three layers known as epidermis, dermis, and fat. Some health issues, such as.

Skin Structure Diagram Best Picture Collection
It is the system that can instantly tell us whether someone is young or old, someone's ethnicity or race or if he/she has been on holidays recently. It also protects us a great deal from harm and allows us to sense our surrounding environment.

Skin topical steroid withdrawal with wheatgrass extract A
Biology Important Diagrams Skin Diagram Skin Diagram The largest organ in the human body is the skin, covering a total area of about 1.8 square meters. The skin is tasked with protecting our body from external elements as well as microbes. Interesting Note:
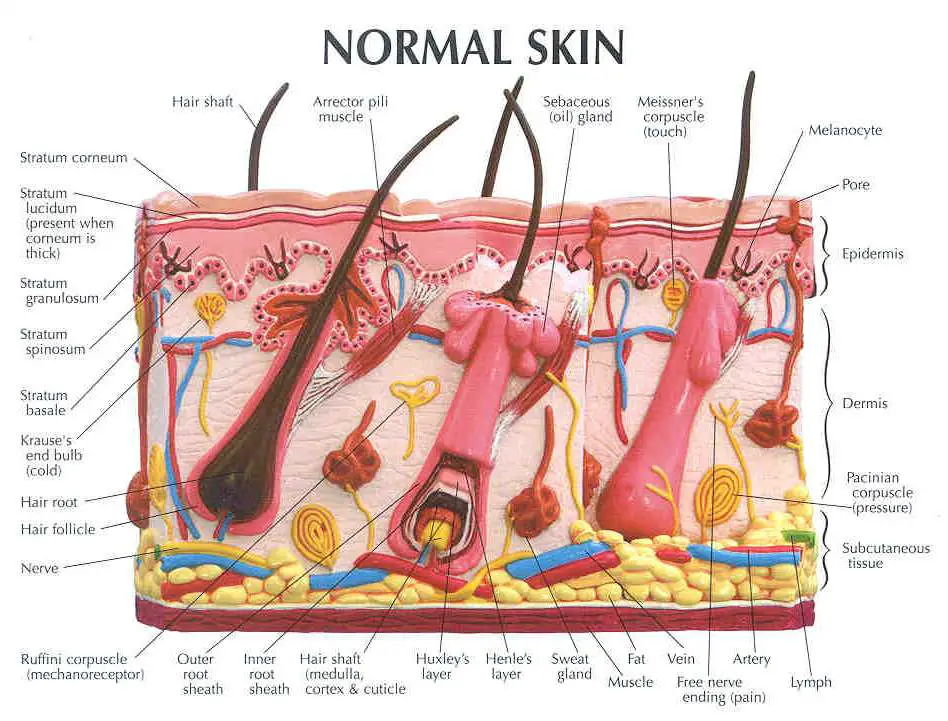
Skin diagram labeled
Skin anatomy and physiology Hair, skin and nails Wound healing Osmosis High-Yield Notes This Osmosis High-Yield Note provides an overview of Skin Structures essentials. All Osmosis Notes are clearly laid-out and contain striking images, tables, and diagrams to help visual learners understand complex topics quickly and efficiently.

The skin Understanding cancer Macmillan Cancer Support
The skin is the body's largest organ. It covers the entire body. It serves as a protective shield against heat, light, injury, and infection. The skin also: Regulates body temperature. Stores water and fat. Is a sensory organ. Prevents water loss. Prevents entry of bacteria.
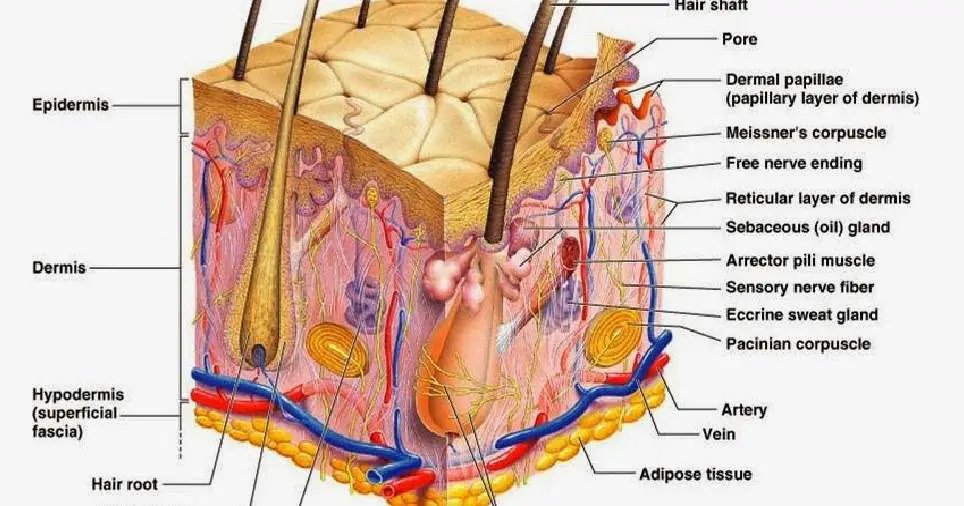
Skin diagram labeled
Functions of the skin. Some of the many roles of skin include: Protecting against pathogens. Langerhans cells in the skin are part of the immune system. Storing lipids (fats) and water. Creating.

Skin anatomy. Human normal skin Background Graphics Creative Market
Stratum Corneum The stratum corneum is the top layer of the epidermis. Its jobs are to: Helps your skin retain moisture Keep unwanted substances out of your body It is made of dead, flattened cells called keratinocytes that are shed approximately every two weeks.
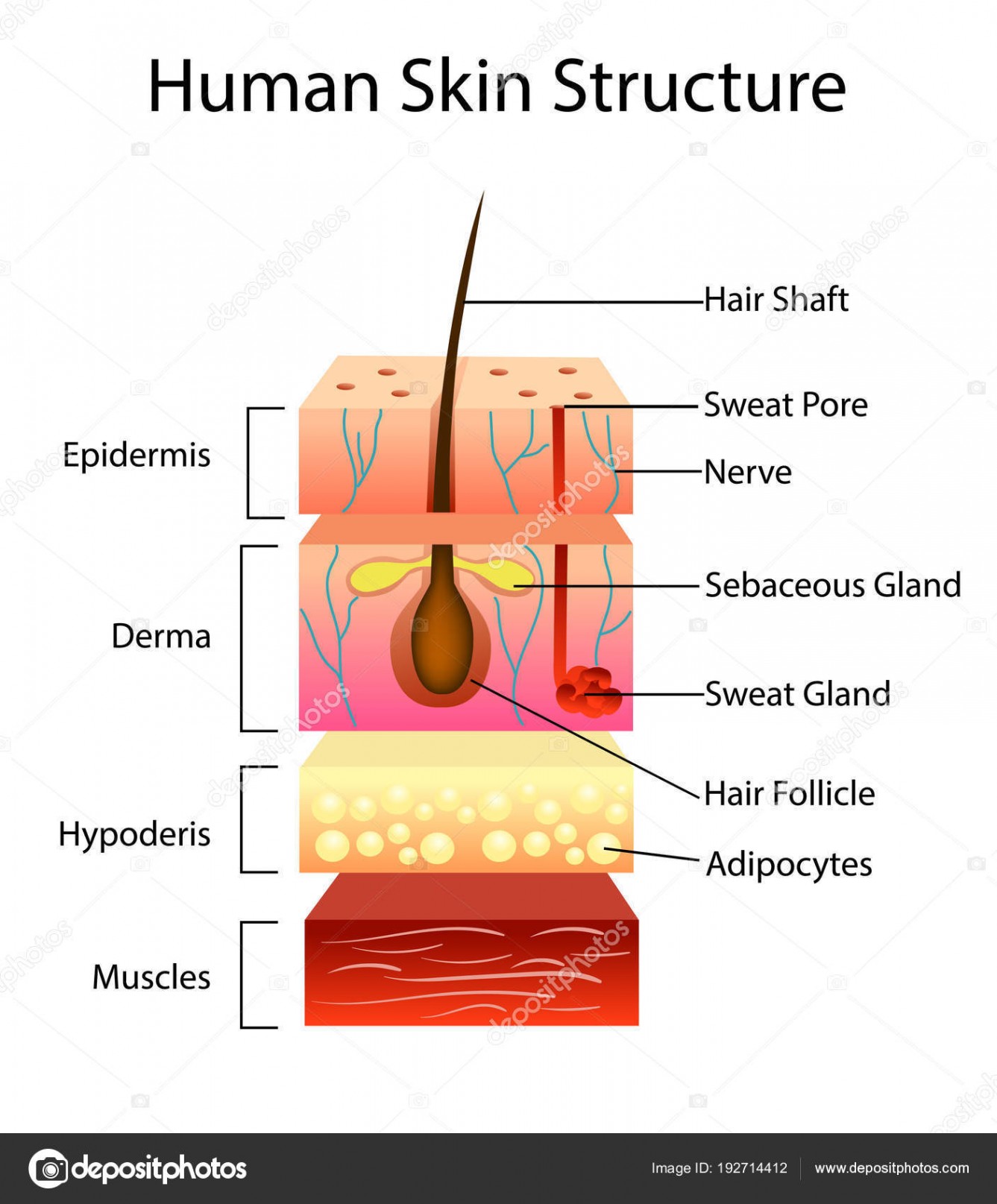
Labelled Pictures Of Human Skin / skin diagram /medical/anatomy/skin
Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous fat layer (hypodermis) Each layer has certain functions. Epidermis The epidermis is the thin outer layer of the skin. It consists of 2 primary types of cells: Keratinocytes. Keratinocytes comprise about 90% of the epidermis and are responsible for its structure and barrier functions. Melanocytes.
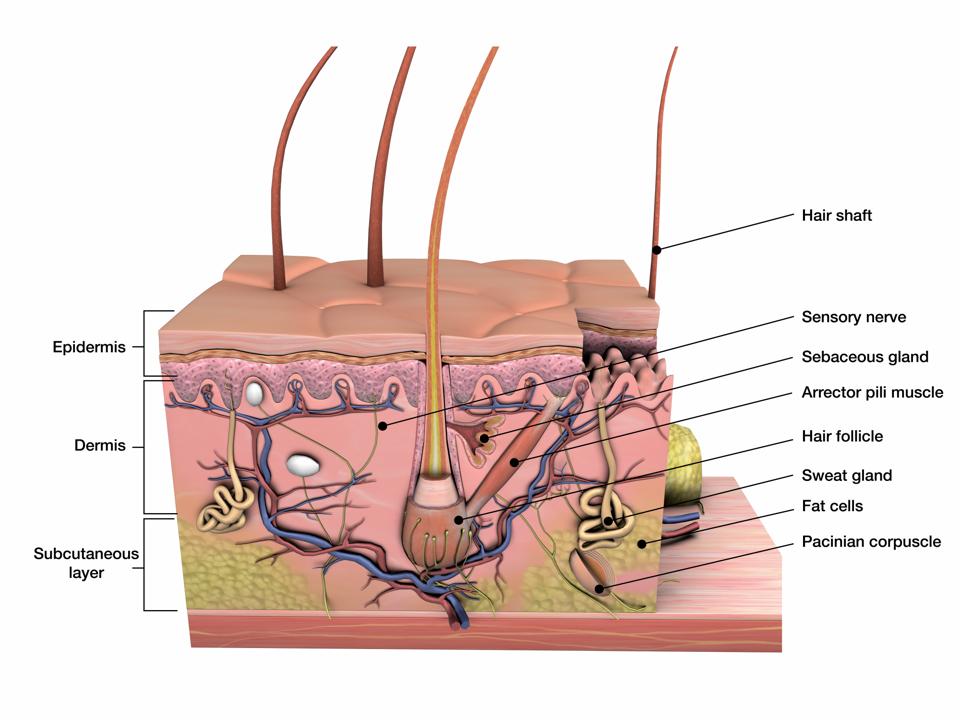
Rep. Ayanna Pressley Reveals Alopecia, What Is This Condition
The thickness of the skin differs over all parts of the body, and between men and women and the young and the old. For example, the skin on the forearm which is on average 1.3 mm in the human male and 1.26 mm in the human female. The Structure of Human Skin Comprises Three Layers. The Three Layers of Skin Are. The outer layer of the skin: Epidermis

Skin Structure (labelled), illustration Stock Image C043/4873
Figure 5.1.1 - Layers of Skin: The skin is composed of two main layers: the epidermis, made of closely packed epithelial cells, and the dermis, made of dense, irregular connective tissue that houses blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures.

Human Skin Anatomy, Labeled Version Stock Vector Illustration of
Psoriasis Albinism Sources + Show all Without the skin, humans would be susceptible to a myriad of pathologies. The organ acts as a protective barrier that limits the migration of microbes and chemicals into the body. Additionally, it plays an integral role in thermoregulation as it participates in evaporation in hyperthermic environments.

Skin Model Labeled Bing Images Skin anatomy, Physiology, Anatomy
The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system.The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue guarding muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs.Human skin is similar to most of the other mammals' skin, and it is very similar to pig skin. Though nearly all human skin is covered with hair follicles, it can appear hairless.
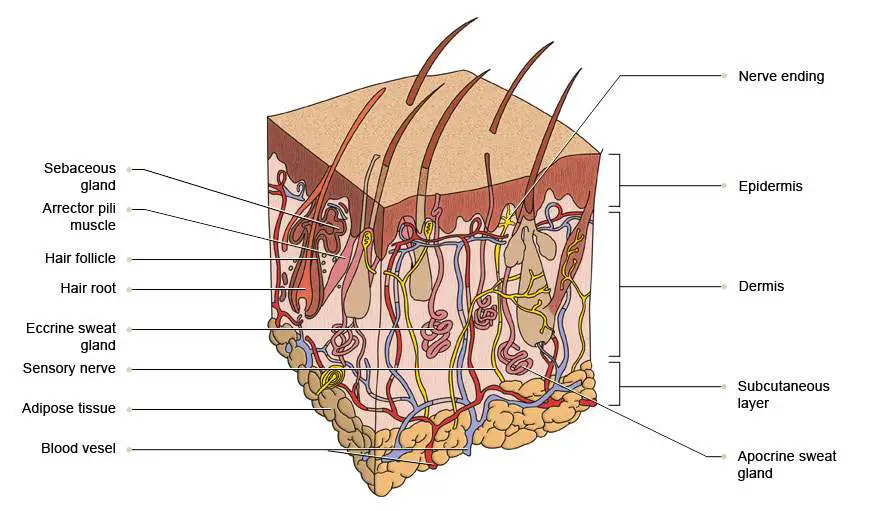
Skin diagram labeled
The skin consists of three layers of tissue: the epidermis, an outermost layer that contains the primary protective structure, the stratum corneum; the dermis, a fibrous layer that supports and strengthens the epidermis; and the subcutis, a subcutaneous layer of fat beneath the dermis that supplies nutrients to the other two layers and that cush.
Skin diagram to label Labelled diagram
The skin is by far the largest organ of the human body, weighing about 10 pounds (4.5 kg) and measuring about 20 square feet (2 square meters) in surface area. It forms the outer covering for the entire body and protects the internal tissues from the external environment. The skin consists of two distinct layers: the epidermis and the dermis.